Processing of PHA
by 3D-printing

In this post, we delve into another prevalent method for plastic processing: 3D-printing. We primarily focus on the innovative and alternative material, PHA (Polyhydroxyalkanoates), and its behavior during the 3D-printing process. Furthermore, we will discuss the advantages and potential of PHA and the challenges and important considerations when selecting this material for 3D-printing.
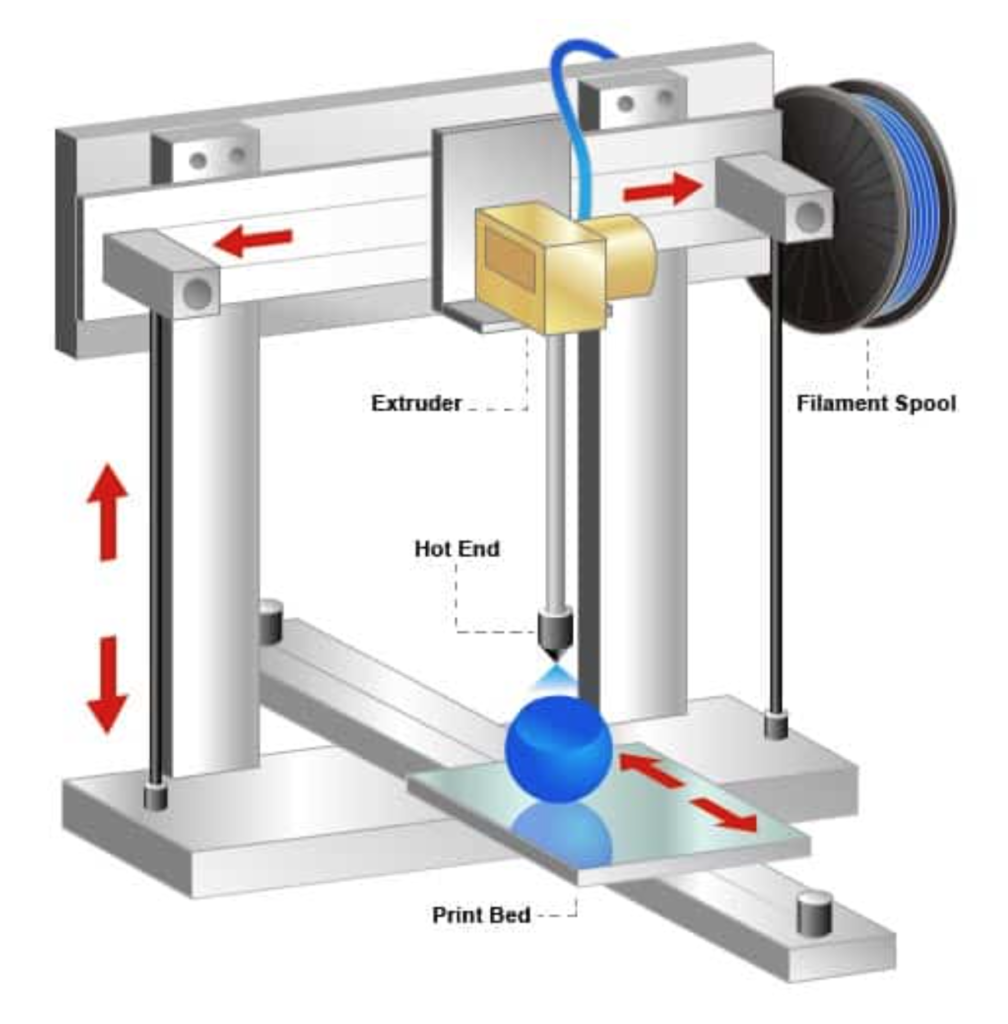
What is 3D-printing?
3D-printing, also known as additive manufacturing (AM), is a process where a three-dimensional object is created from a digital file. The object is built layer by layer, allowing for complex shapes and designs. This technique is widely used for prototyping, custom manufacturing, and in industries such as aerospace, medical, and automotive.
PHA has made its first introduction in 3D Printing as well, as an alternative to for PLA and ABS, ensuring printability and a high Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT).
What is PHA?
PHA (Polyhydroxyalkanoates) is a bio-based polymer produced naturally by bacteria during their growth phase, also known as fermentation. Its environmentally friendly properties make it a compelling alternative to traditional plastics. PHA can be composted and is readily biodegradable in various environments without leaving harmful residues, like microplastics, making it a sustainable and responsible choice for plastic replacement.
How does PHA behave in 3D-printing?
While most PHA types can be processed similarly to other plastics, there are some unique characteristics to consider.
For instance, PHA has a lower melting temperature than many conventional plastics, meaning it consumes less energy. However, most PHA types also require longer cooling periods to facilitate the polymer’s crystallization, Typically during 3D Printing PHA requires stronger blowing fans and a cold print plate. Furthermore, PHA is more sensitive to moisture and high-shear rates than most other plastics, which can result in quality issues with the final product if not handled correctly within its proper processing window. Hence, it requires careful storage and preparation, like pre-drying, to ensure optimal results.
Together with our in-house partner colorFabb, we have developed a fully PHA-based 3D Printing polymer, called allPHA. For tips and tricks have a look at their website.
Conclusion
Proper 3D-printing of PHA requires a thorough understanding of the material and its unique properties, as well as modifications to the standard processes. However, with its environmentally friendly attributes and potential for high production speeds, PHA undoubtedly offers the potential to become a more sustainable and efficient alternative to traditional plastics. With the right knowledge, preparation, and attention to detail, the use of PHA in 3D-printing can be a profitable, sustainable, and responsible choice for the future of plastic production.
Home of PHA
Interested in learning more about PHA and its role in 3D-printing? Our team of experts is ready to assist you in exploring this innovative material and its potential in your manufacturing processes.
